
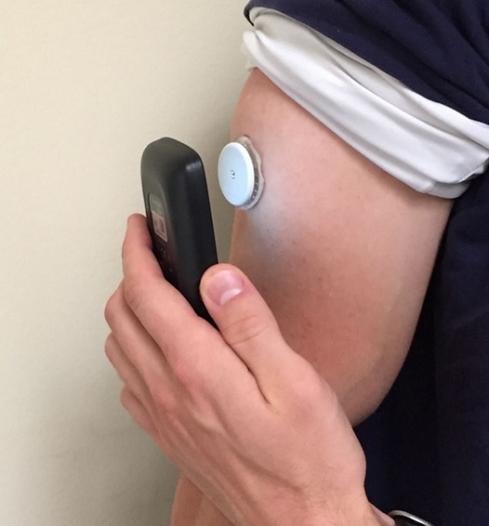
Data stored in the sensor are transmitted on demand to a "reader" held within a centimeter or two of the sensor unit, employing near-field communication (NFC) technology. The sensor measures the glucose level of interstitial fluids (as a proxy for blood sugar levels) continuously up to eight hours of these readings, averaged over each 15-minute period, are stored in the sensor unit, unlike most other CGM systems, which use a wireless link (typically Bluetooth) to an external device for each reading.
#Freestyle libre flash glucose monitoring system fda skin
The original Freestyle Libre monitor introduced by Abbott Diabetes Care in 2015 was described as doing "flash glucose monitoring," with a disposable 14-day sensor probe under the skin (as with other CGM sensors), but factory-calibrated without requiring calibration against a finger-stick glucose test. This lag time varies based on the person and the device, and is generally 5–20 minutes. As it takes time for glucose to travel from the bloodstream into the interstitial fluid, there is an inherent lag behind the current blood glucose level and the level measured by the CGM. Īnother limitation is that glucose levels are taken from the interstitial fluid rather than the blood. Some manufacturers warn users of relying only on CGM-measurements and the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends to validate hypoglycaemic values via fingerprick testing of blood glucose level. Still, on the Cochrane systematic review mentioned above, the use of continuous glucose monitors did not increase the risk of hypoglycaemia or ketoacidosis.
This is especially problematic as some devices offer alarm functions to warn of hypoglycemic episodes and people might rely on those alarms. However, there are important limitations: CGM systems are not sufficiently accurate for detecting hypoglycemia, a common side-effect of diabetes treatment. However, the use of continuous glucose monitors appears to lower hemoglobin A1c levels, more than just monitoring through capillary blood testing, particularly when used by individuals with poorly controlled diabetes together with an integrated insulin pump. Ī Cochrane systematic review found that there is limited and conflicting evidence of the effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring systems in children, adults or patients with poorly controlled diabetes. Some studies have demonstrated reduced time spent in hypoglycemia or a lower glycated hemoglobin, both favorable outcomes. ĬGM is an increasingly adopted technology which has shown to have benefits for people with diabetes. Some CGM devices have to be periodically calibrated by users with traditional blood glucose measurements, while some do not require user calibration. CGM use allows trends in blood glucose to be displayed over time. Traditional fingerprick testing of blood glucose levels measures the level at a single point in time. This electric current (proportional to the glucose concentration) is then relayed from a transmitter attached to the sensor out to a reader which displays the data to the patient. Currently approved CGMs use an enzymatic technology which reacts with glucose molecules in the interstitial fluid generating an electric current. A continuous glucose monitor consists of three parts: a small electrode placed under the skin, a transmitter sending readings at regular intervals (ranging from every 5 to 15 min), and a separate receiver.


people with type I, type II diabetes or other types of diabetes (e.g.

The sensor and transmitter are fixed to the upper arm and the receiver shows current blood glucose level and a graph of recent blood glucose levels.Ī continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device used for monitoring blood glucose on a continual basis by insulin-requiring people with diabetes, e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
